Step 1:
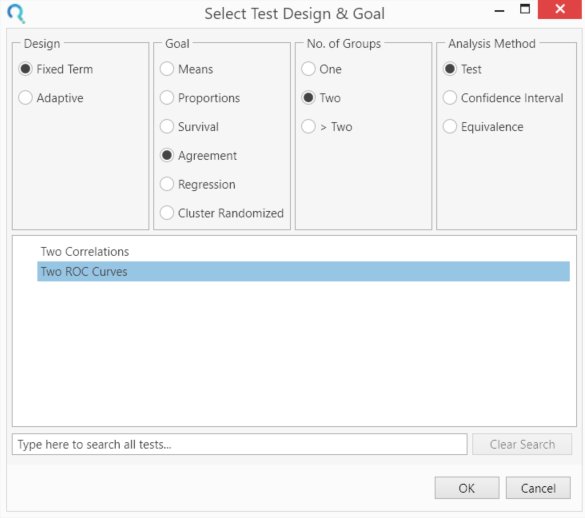
Select the 'Two ROC Curves' from the Study Design Pane.
This can be done using the radio buttons or alternatively, you can use the search bar at the end of the Select Test Design & Goal window.
Step 2:
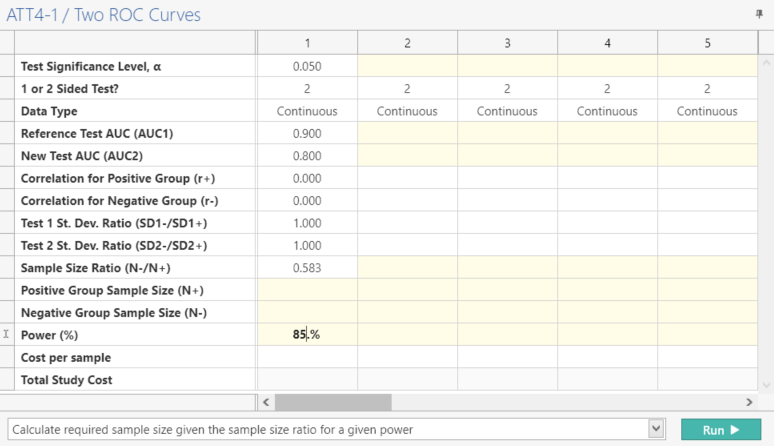
Enter the parameter values for sample size calculation taken from the study design.
Step 3:
Select “Calculate required overall sample size given the sample size ratio (N-/N+) for a given power”, click the “Run” button to solve for the sample size.
| This gives a sample size of 120 positive cases and 70 negative cases as per the study design. |

Note: When using nQuery Advanced, both the Positive and Negative Sample Size will be auto-calculated once the Power (%) value is entered.
Step 4:
Once the calculation is completed, nQuery Advanced provides an output statement summarizing the results. It States:
| Output Statement: |
|
“In a two sided test comparing the area under the ROC curve (AUC) of a reference test to a proposed test for continuous response data using a z-test approximation, a sample size of 120 from the positive group (with the condition) and a sample size of 70 from the negative group (without the condition) achieves 85.23% power at the 5% significance level when the AUC for both tests under the null hypothesis is 0.9 and the AUC for the proposed test under the alternative hypothesis is 0.8. This assumed that the correlation between the test scores for subjects from the positive group is 0 and the correlation between subjects from the negative group is 0.”
|
















