

Scientific intelligence platform for AI-powered data management and workflow automation


Scientific intelligence platform for AI-powered data management and workflow automation

Objective: We performed a double-blind, double-placebo–controlled, randomized trial involving women with idiopathic urgency urinary incontinence who had five or more episodes of urgency urinary incontinence per 3-day period, as recorded in a diary. For a 6-month period, participants were randomly assigned to daily oral anticholinergic medication (solifenacin, 5 mg initially, with possible escalation to 10 mg and, if necessary, subsequent switch to trospium XR, 60 mg) plus one intradetrusor injection of saline or one intradetrusor injection of 100 U of onabotulinumtoxinA plus daily oral placebo. The primary outcome was the reduction from baseline in mean episodes of urgency urinary incontinence per day over the 6-month period, as recorded in 3-day diaries submitted monthly. Secondary outcomes included complete resolution of urgency urinary incontinence, quality of life, use of catheters, and adverse events.
Year: 2012
Source: New England Journal of Medicine
Link: http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1208872
Clinical Area: Urology
| Sample Size Section in Paper/Protocol: |
|
“A sample size of 242 subjects (121 per treatment group) provides at least 80% power to detect a relative difference of 53% between botulinum toxin A and standardized anticholinergic therapy, assuming a treatment difference of -0.80 and a common SD of 2.1 (effect size = 0.381), and a two-sided type I error rate of 5%. Sample size has been adjusted to allow for a 10% loss to follow-up over the 6-months of treatment as well as one interim analysis to stop early for benefit.” |
Note:
From Table 6 of Protocol:
Mean for ACH Group: -1.5, Mean for OnabotulinumtoxinA group: -2.3
Summary of Necessary Parameter Estimates for Sample Size Calculation:
| Parameter | Value |
| Significance Level (2-Sided) | 0.05 |
| Expected OnabotulinumtoxinA Mean | -2.3 |
| Expected Antichollnergic Therapy Mean | -1.5 |
| Standard Deviation (Both Groups) | 2.1 |
| Power | 80% |
| Number of Interim Analyses | 1 |
| Alpha Spending Function (from Protocol) | O'Brien-Fleming |
| Expected Dropout | 10% |
Step 1:
Select the Group Sequential Test of Two Means table from the Select Test Design & Goal window.
This can be done using the radio buttons or alternatively, you can use the search bar at the end of the Select Test Design & Goal window.
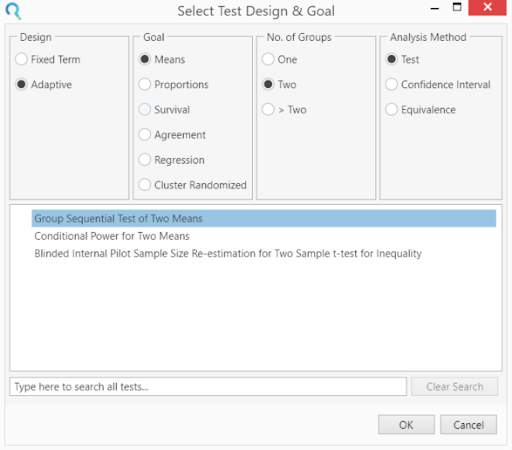
Step 2:
Enter the parameter values for sample size calculation taken from the study protocol.
Setting the “Number of looks” row to two specifies one interim analysis and one endpoint analysis.
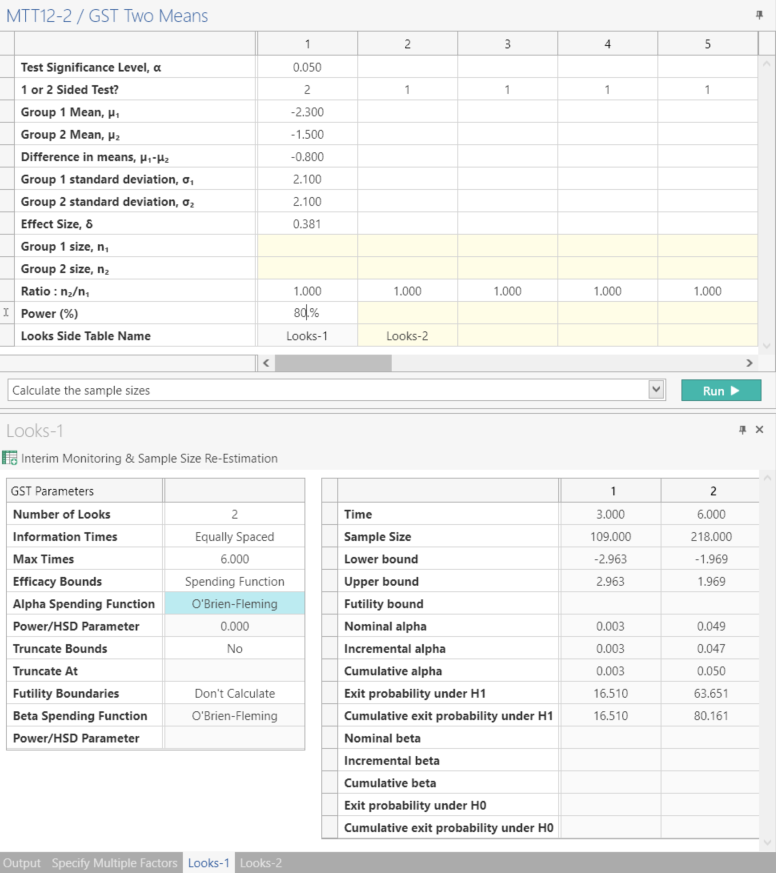
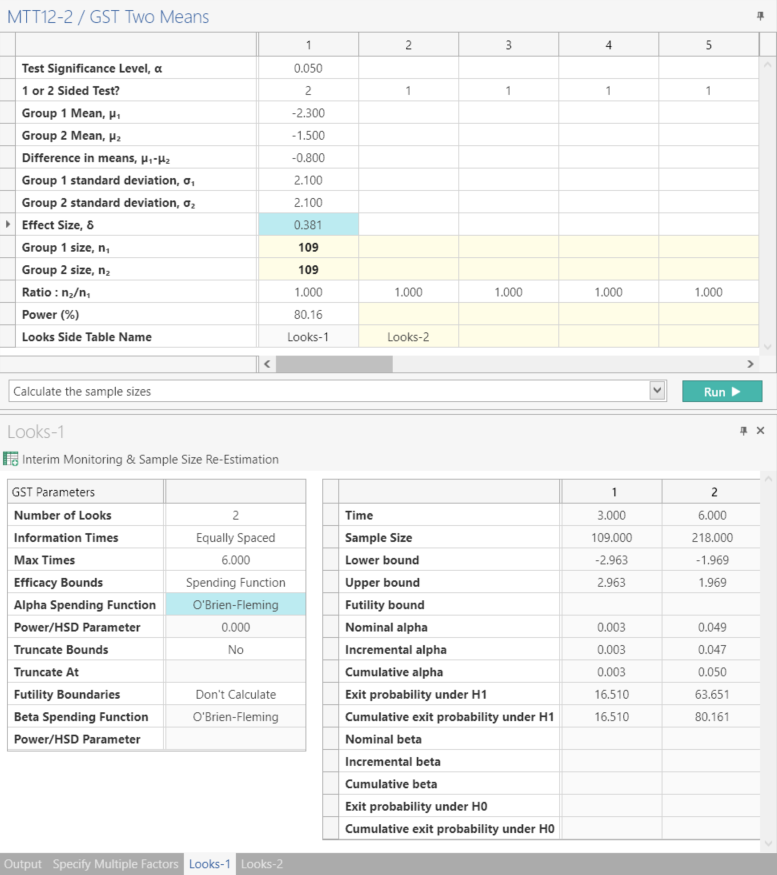
Step 3:
Click Run to solve for Sample Size
| This analysis calculates a sample size of 109 patients per group with a power of 80.15%. |
Step 4:
Once the calculation is completed, nQuery Advanced provides an output statement summarizing the results. It States:
| Output Statement: |
|
Sample sizes of 109 in group 1 and 109 in group 2 are required to achieve 80.16% power to detect a difference in means of -0.8 (the difference between group 1 mean, μ1, of -2.3 and group 2 mean, μ2, of -1.5) assuming that the standard deviation in group 1 is 2.1 and in group 2 is 2.1 using a two-sided z-test with 5% significance level. These results assume that the group sequential design has 1 interim sequential tests (2 total interim looks including final analysis) and the O'Brien-Fleming spending function is used to determine the efficacy test boundary. The drift parameter for this design equals 2.813. The drift parameter defines the increase in sample size needed over a fixed term design and equals square root of the maximum information level by the difference. |

Step 5:
Calculate the sample size adjusted for expected 10% dropout, as outlined in protocol.
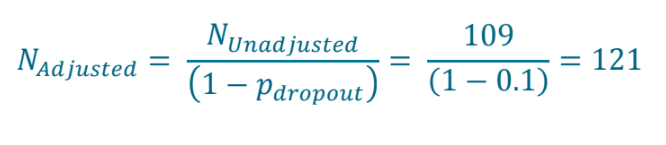
| This gives a final sample size of 121 per group as per study design in protocol. |
Copyright © Statsols. All Rights Reserved. Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information. Privacy Policy .