

Scientific intelligence platform for AI-powered data management and workflow automation


Scientific intelligence platform for AI-powered data management and workflow automation

Objective: Our primary objective is to determine the clinical efficacy of PHiD-CV in reducing respiratory exacerbations in children aged 18 months to 14 years with recurrent PBB, CSLD or bronchiectasis.
Year: 2013
Source: Trials
Link: https://trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1745-6215-14-282
Clinical Area: Respiratory
| Sample Size Section in Paper/Protocol: |
|
“Prospective data collected in Brisbane children with non-CF bronchiectasis indicate a mean annual incidence of 2.1 (standard deviation 1.046) exacerbations requiring hospital clinic attendance or hospitalisation. PHiD-CV efficacy against exacerbations in children with bronchiectasis is unknown. However, based on the aforementioned pilot data and AOM data from the POET study (30% reduction) [33], our trial is powered to detect a 30% reduction from 2.1 to 1.47 exacerbations in the 12 months following the second vaccine dose. Assuming a Poisson distribution, 93 children per group will provide 90% power (α = 0.05, two-sided) to detect a 30% reduction in exacerbations in the PHiD-CV group and 80% power to detect a 25% reduction. Assuming a 10% loss to follow-up, we will recruit 206 children (103 per group). Differences of less than 20% are unlikely to change clinical practice without additional supporting evidence.” |
Summary of Necessary Parameter Estimates for Sample Size Calculation:
| Parameter | Value |
| Significance Level (1-Sided) | 0.025 |
| Control Group Rate | 2.1 |
| Rate Ratio | 0.7 |
| Exposure Time (years) | 1 |
| Allocation Ratio | 1 |
| Power | 90% |
| Expected Dropout | 1% |
Step 1:
Select the Test for the Ratio of Two Incidence Rates using the Poisson Model from the Select Test Design & Goal window.
This can be done using the radio buttons or alternatively, you can use the search bar at the end of the Select Test Design & Goal window.
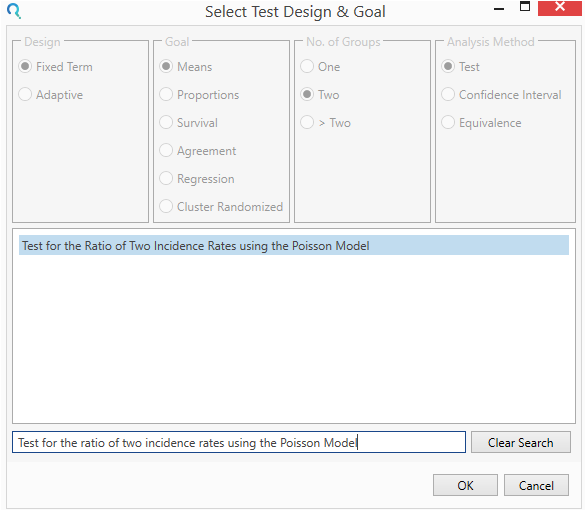
Step 2:
Enter the parameter values for sample size calculation taken from the study protocol.
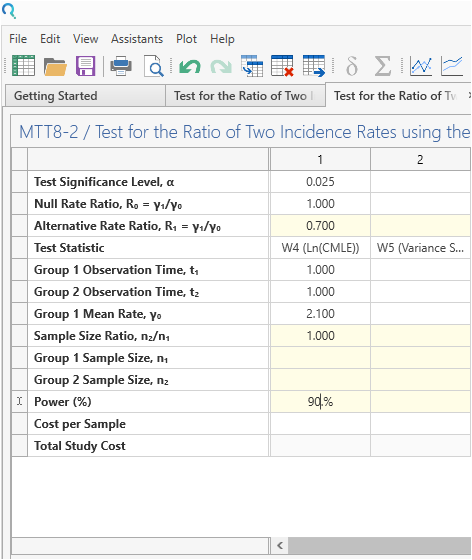
Step 3:
Select Run to solve for sample size.
| This gives a sample size of 93 per group, as per the study protocol. |
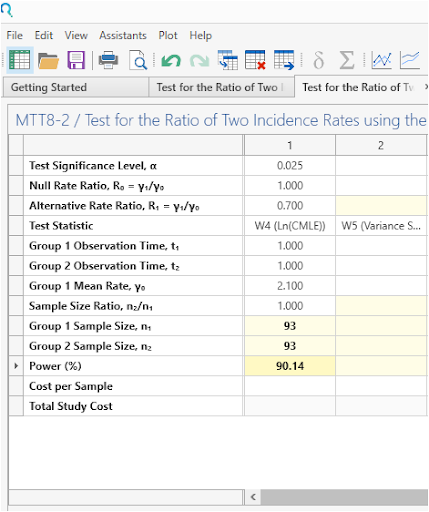
Step 4:
Once the calculation is completed, nQuery Advanced provides an output statement summarizing the results. It States:
| Output Statement: |
|
In a study testing ratio of independent two incidence rates under a Poisson model rate, a sample of 93 subjects in group 1 observed for 1 time periods and a sample of 93 subjects in group 2 observed for 1 time periods achieves 90.14% power to detect an incidence rate ratio (γ₁/γ₀) of 0.7 (assuming the incidence rate ratio is 1 under the null hypothesis) when the mean incidence rate for group 1 is 2.1 at the 0.025 significance level using a one-sided test. This was done under the assumption that the test statistic would be the ln(CMLE). |

Copyright © Statsols. All Rights Reserved. Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information. Privacy Policy .